With over 10,000 backlinks since the post was published, it’s fair to say that the Skyscraper Technique took the world by storm in 2015. But what is it exactly, how can you implement it, and can you still get results with this technique in 2023?
Let’s get started.
The Skyscraper Technique is a link building strategy where you improve existing popular content and replicate the backlinks.
Brian named it so because in his words, “It’s human nature to be attracted to the best. And what you’re doing here is finding the tallest ‘skyscraper’ in your space… and slapping 20 stories to the top of it.”
Here’s how the technique works:
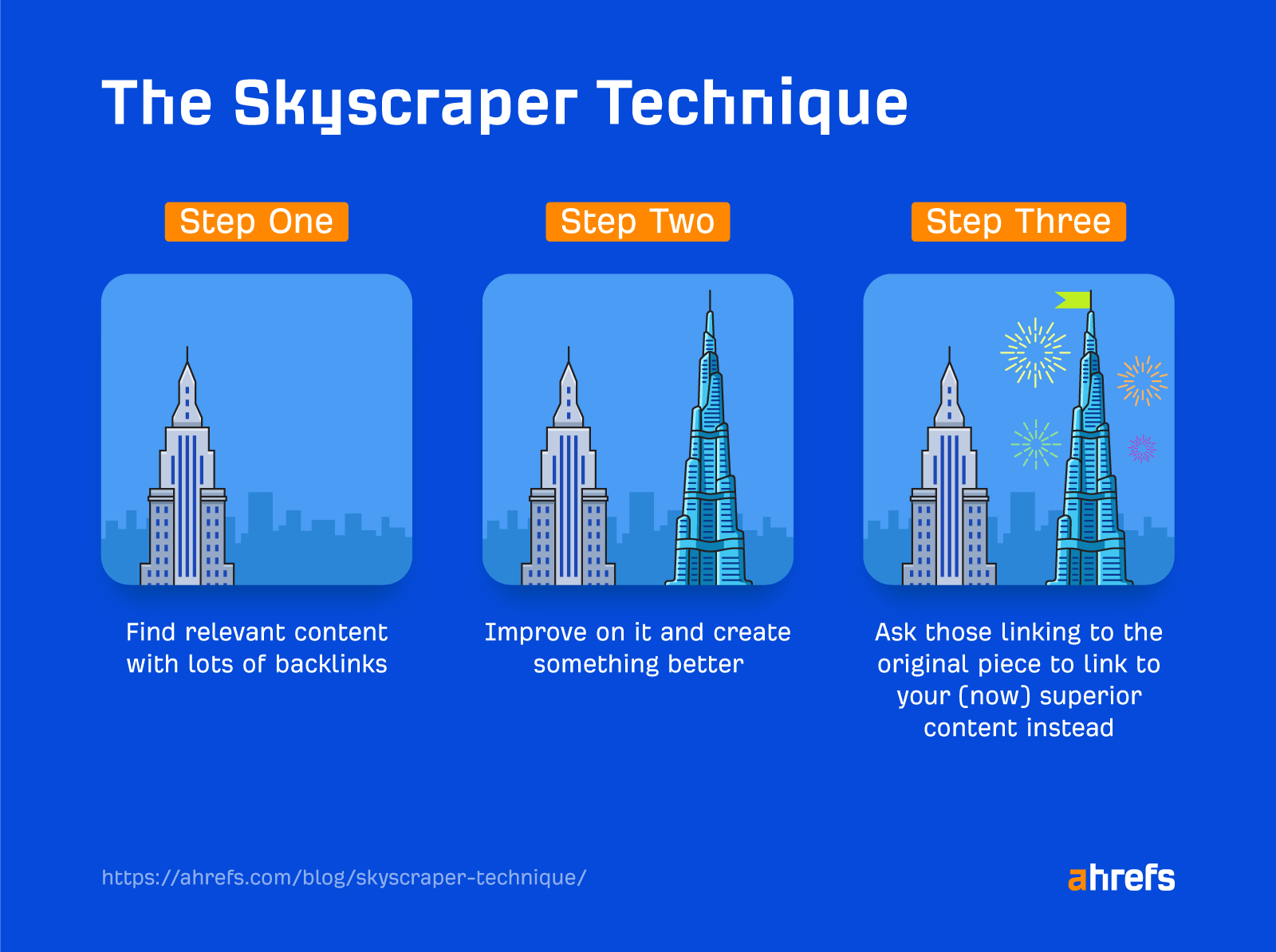
Follow these three steps to execute the Skyscraper Technique.
1. Find relevant content with lots of backlinks
There are three methods to find relevant pages with plenty of links:
Use Site Explorer
Enter a popular site into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. Next, go to the Best by backlinks report.
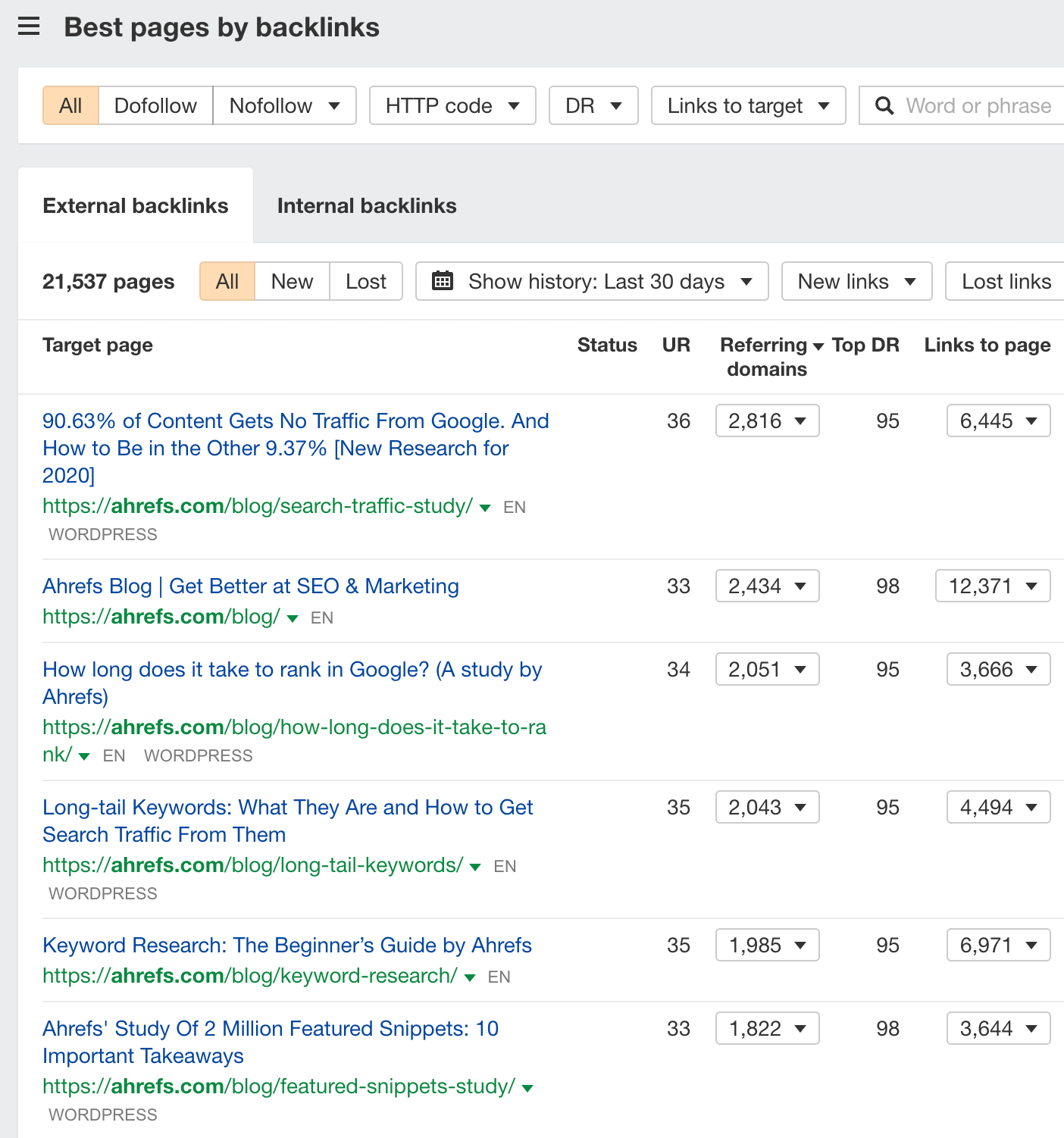
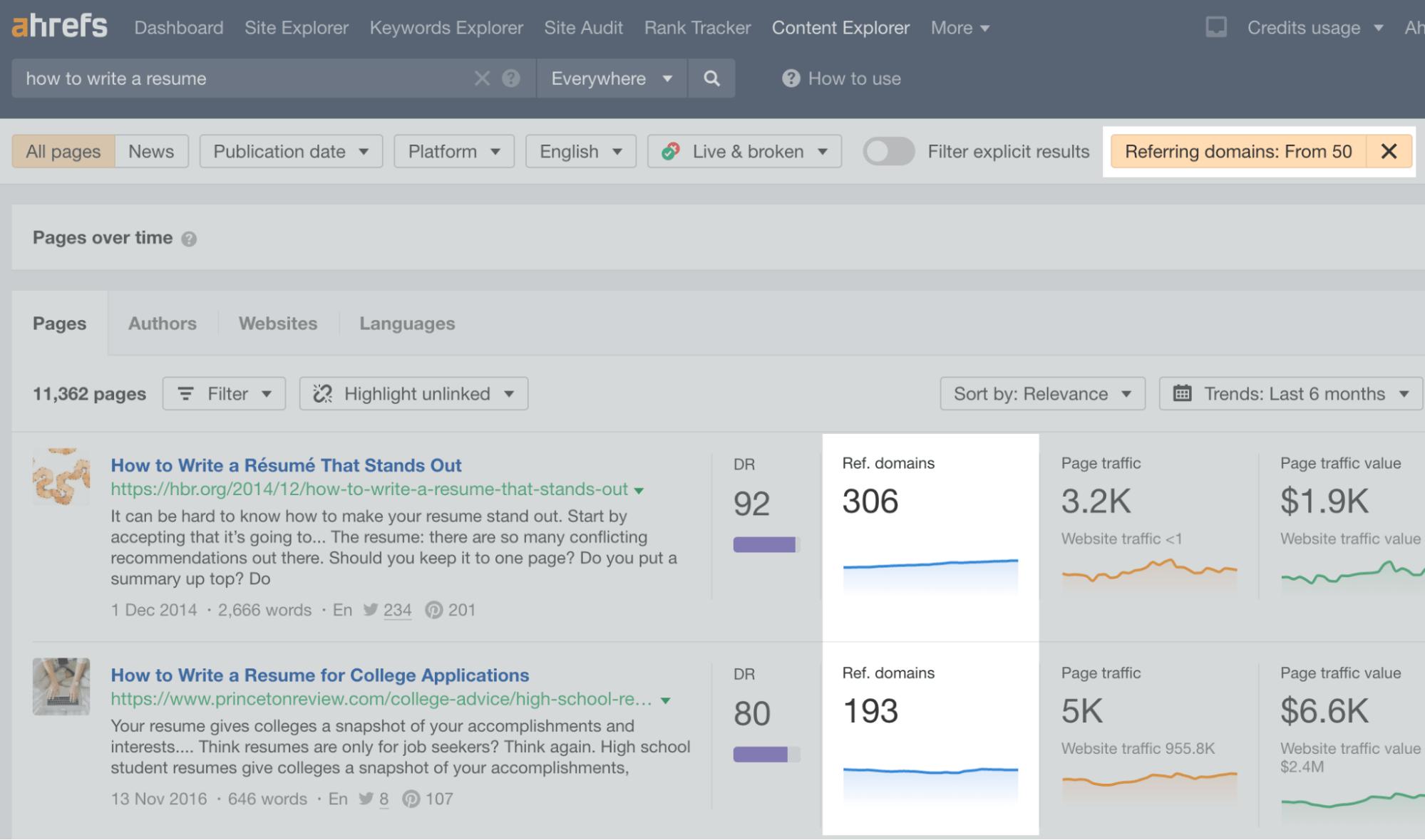
This report shows you a list of pages from the site with the highest number of referring domains. If there are content pieces with more than 50 referring domains, they’re likely to be good potential targets.
Use Content Explorer
Ahrefs’ Content Explorer is a searchable database of 10 billion pages. You can use it to find mentions of any word or phrase.
Let’s start by entering a broad topic related to your niche into Content Explorer. Next, set a Referring domains filter to a minimum of 50.
We can also add:
- Language filter to get only pages in our target language.
- Exclude homepages to remove homepages from the results.
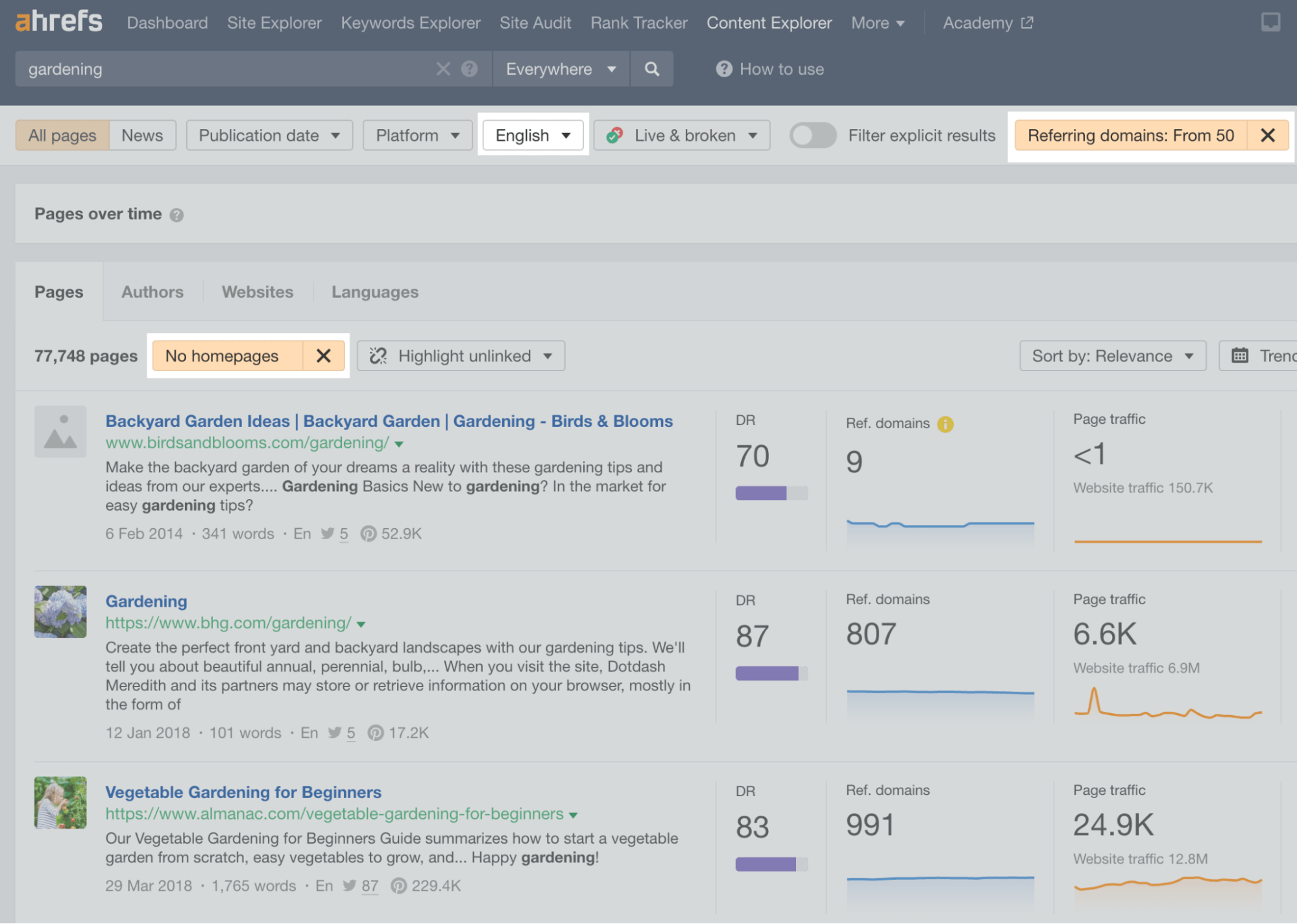
Eyeball the results to see if there are any potential pieces of content you could beat.
Use Keywords Explorer
Enter a broad keyword into Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. Next, go to the Matching terms report and set a Keyword Difficulty (KD) filter to a minimum of 40.
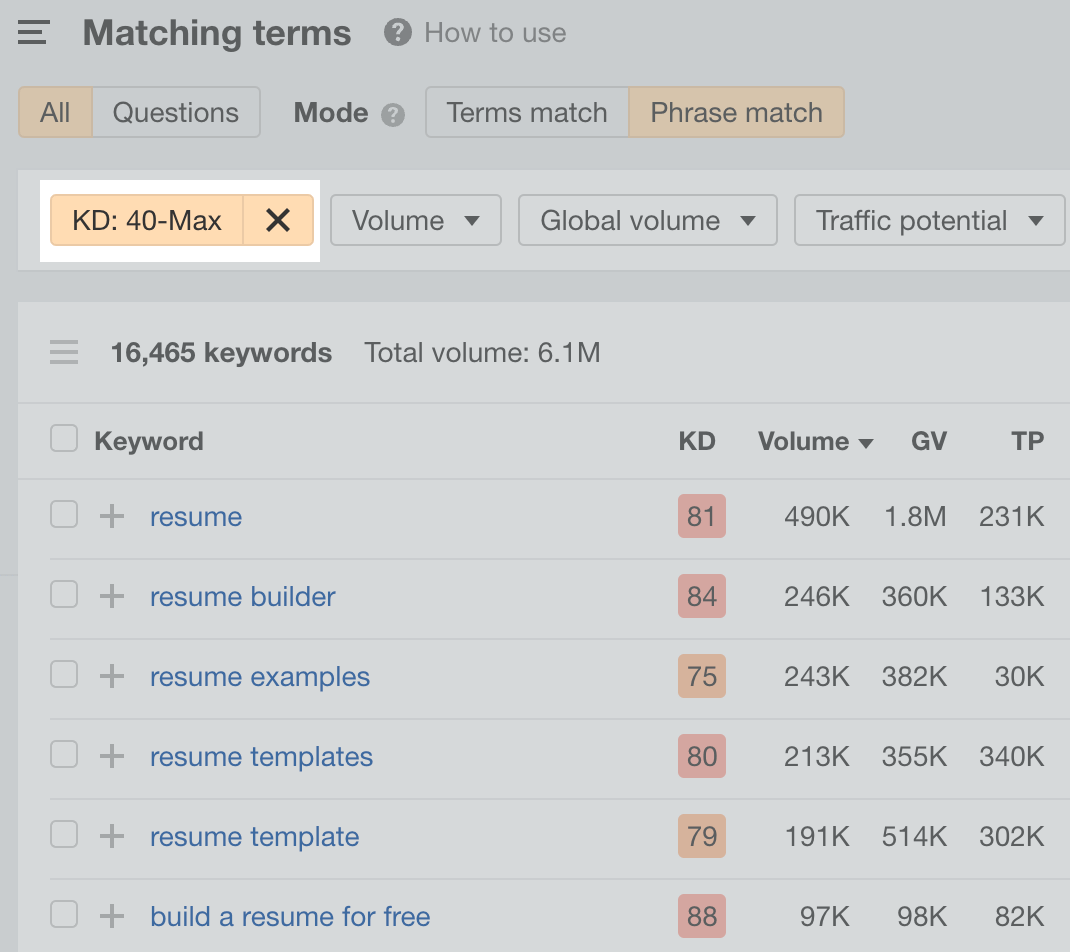
Why filter for KD?
The reason is due to the method we use at Ahrefs to calculate KD. Our KD score is calculated from a trimmed mean of referring domains (RDs) to the top 10 ranking pages.
In other words, the top-ranking pages for keywords with high KD scores have lots of backlinks on average.
From here, you’ll want to go through the report to find potential topics you could build a better piece of content around.
2. Make it better
The core idea (or assumption) behind the Skyscraper Technique is that people want to see the best.
Once you’ve found the content you want to beat, the next step is to make something even better.
According to Brian, there are four aspects worth improving:
- Length – If the post has 25 tips, list more.
- Freshness – Update any outdated parts of the original article with new images, screenshots, information, stats, etc.
- Design – Make it stand out with a custom design. You could even make it interactive.
- Depth – Don’t just list things. Fill in the details and make them actionable.
3. Reach out to the right people
The key to successfully executing the Skyscraper Technique is email outreach. But instead of spamming everyone you know, you reach out to those who have already linked to the specific content you have improved.
The assumption: Since they’ve already linked to a similar article, they’re more likely to link to one that’s better.
You can find these people by pasting the URL of the original piece into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer and then going to the Backlinks report.
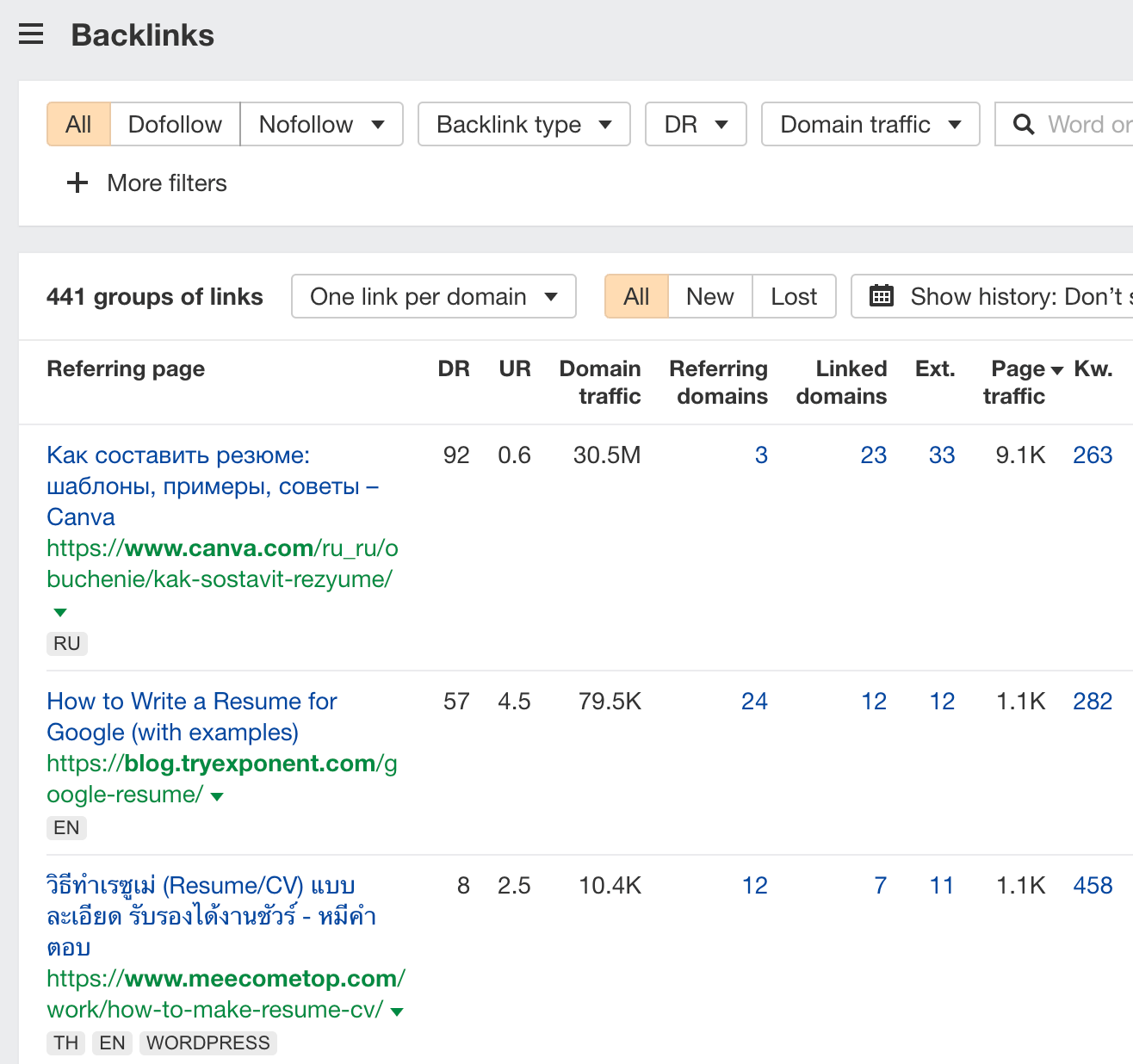
This report shows all the backlinks to the page. In this case, there are 441 groups of links.
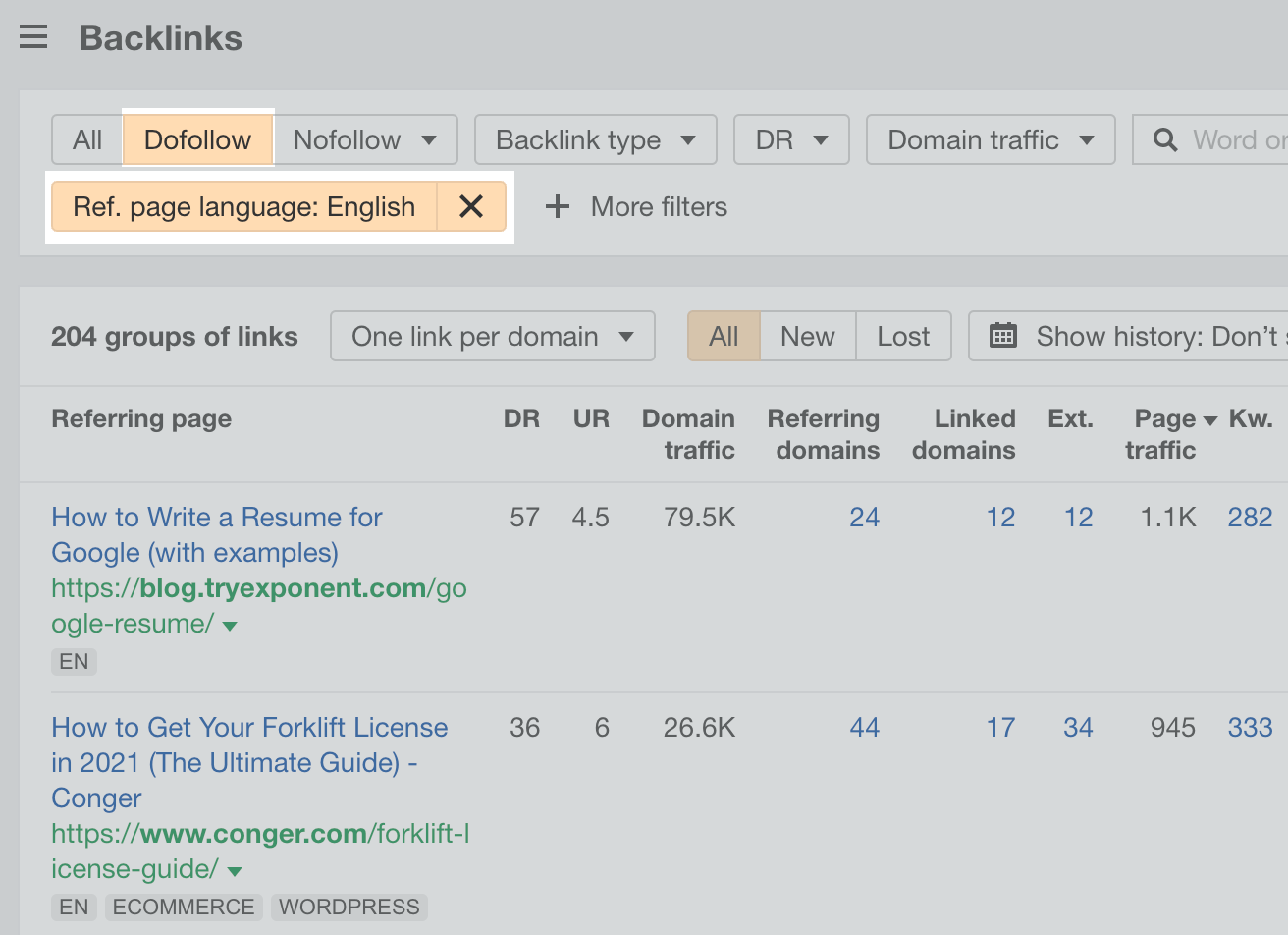
But not all of these links will make good prospects. So you’ll likely need to add some filters to clean them up. For example, you can:
- Add a Language filter for the language you’re targeting (e.g., English).
- Switch the tab to Dofollow for equity-passing links.
It’s been roughly eight years since Brian shared this link building strategy. Honestly speaking, the technique has been oversaturated. Given its widespread use, its effectiveness may even be limited.
Some SEOs even say they wouldn’t recommend it.
So we asked our Twitter and LinkedIn following this question and received 1,242 votes. Here are the results:
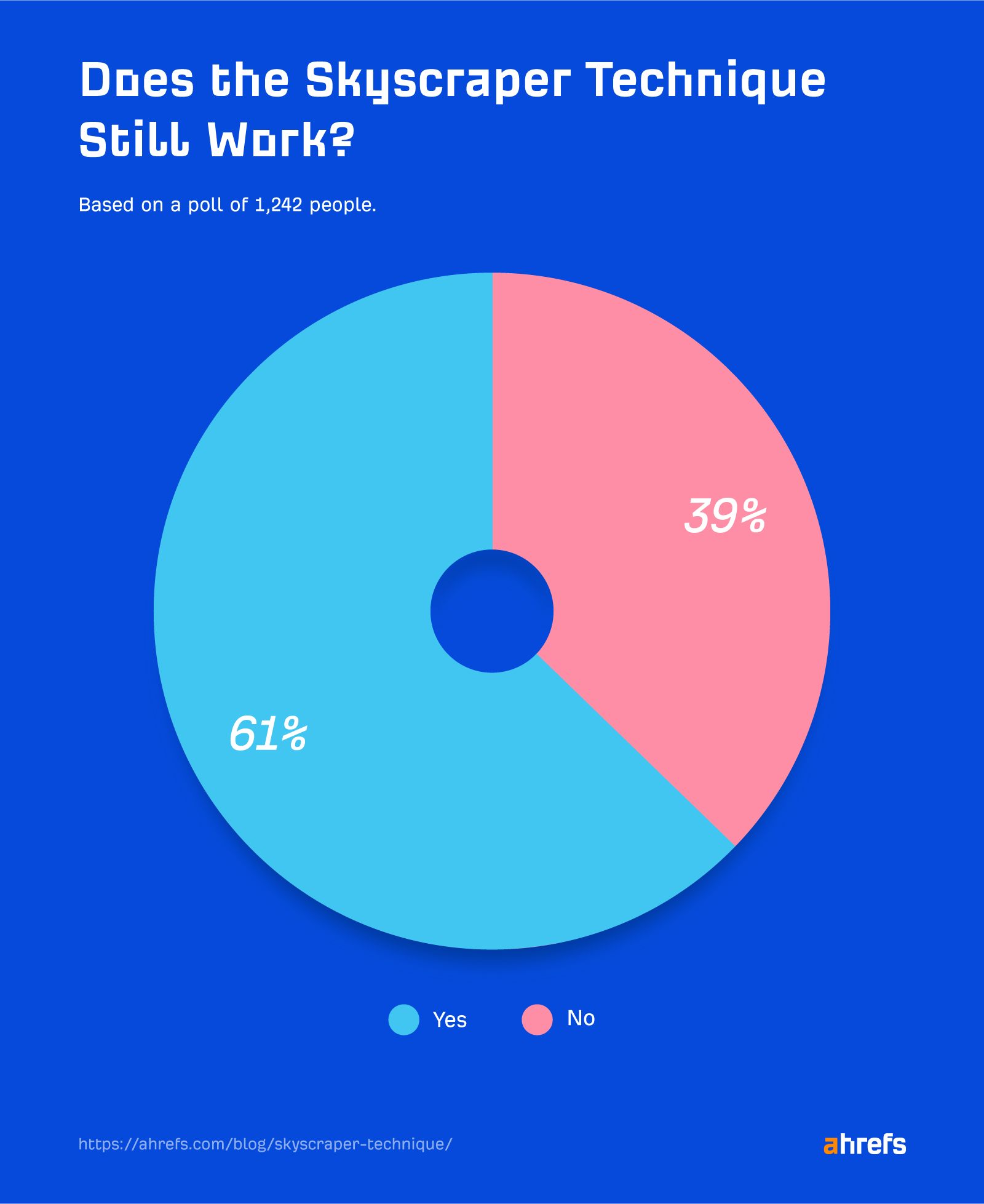
Clearly, many SEOs and marketers still believe the technique works.
Fundamentally, it makes sense that the Skyscraper Technique still works. After all, the principles are the same behind (almost) any link building strategy:
- Create great content
- Reach out to people and promote it
But why do people think it’s no longer effective? There are a few reasons why and knowing them will help you improve your chances of success with the Skyscraper Technique.
Let’s start with:
1. Sending only Brian’s email template
In Brian’s original post, he suggested an email template for his readers to use:
Hey, I found your post: http://post1
<generic compliment>
It links to this post: http://post2
I made something better: http://post3
Please swap out the link for mine.
Unfortunately, many SEOs decided to use this exact template word for word.
Link building doesn’t exist in a vacuum. If everyone in your niche decides to send this exact template to every possible website, it’ll burn out real fast. And that’s exactly what happened.
Now, if a website owner sees this template, chances are they’ll delete it right away.
I’m not saying this to disparage templated emails. If you’re sending something at scale, templating is necessary. But move away from this template. Write your own, personalize it as much as possible, and follow the outreach principles here.
Even better, ask yourself:
“What makes my content unique and link-worthy?”
2. Not segmenting your prospects
People link for different reasons, so you shouldn’t send everyone the same pitch.
Consider dividing your list of prospects into segments according to the context in which they linked. You can do this by checking the Anchors report in Site Explorer.
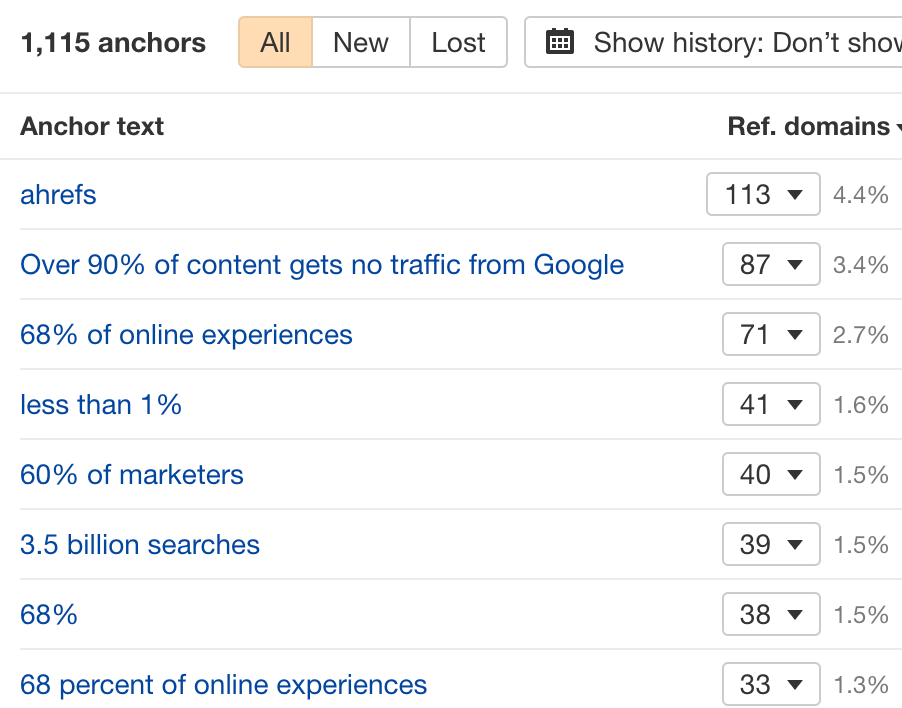
You can clearly see people are linking to different statistics from our SEO statistics post. So, for example, if we were doing outreach for a hypothetical post, we might want to mention to the first group that we have a new statistic for “Over 90% of content gets no traffic from Google.”
Then, to the second group, we’ll mention that we have new statistics for “68% of online experiences.” And so on.
In fact, that’s exactly what we did when we built links to this post. Check out the case study here:
3. Not reaching out to enough people
Ultimately, link building is still a numbers game. If you don’t reach out to enough people, you won’t get enough links.
Simply put: You need to curate a larger list of link prospects.
So rather than limiting yourself to only replicating the backlinks of the original content, you should replicate the backlinks from other top-ranking pages covering the same topic too.
To find these pages, enter the target keyword into Keywords Explorer and scroll down to the SERP overview.
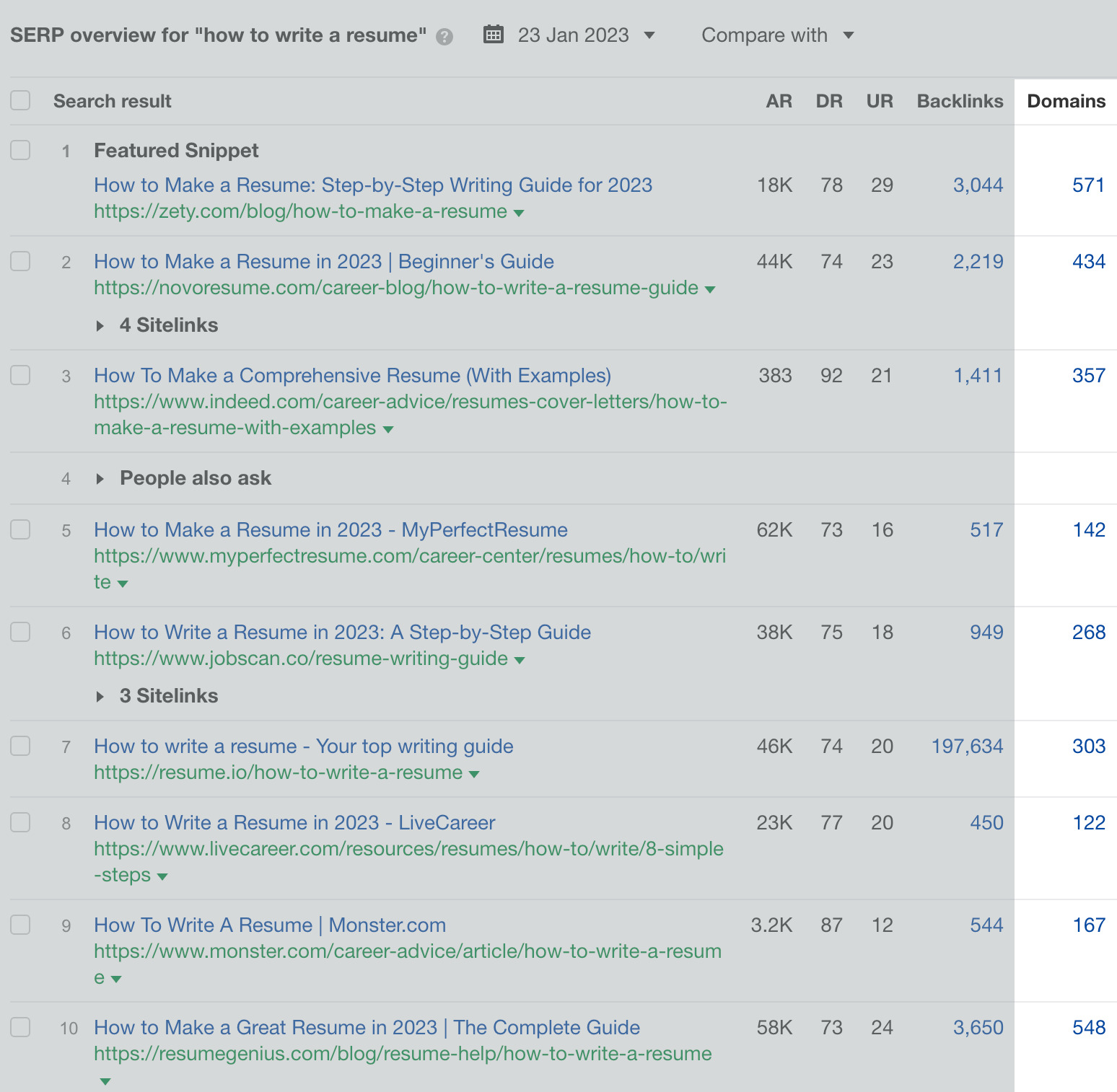
In this example, most top-ranking pages have tons of links, and all of them (after filtering, of course) could be potential link prospects.
Search for your keyword, set a Referring domains filter, and you’ll see relevant pages where you can “mine” for more skyscraper prospects.
4. Thinking bigger equals better
Someone creates a list with 15 tools. The next person ups it to 30. Another “skyscrapers” it to 50, and the next increases it to 100.
Not only is it a never-ending arms race, there’s also no value for the reader.
No one wants to skim through 5,000 words or hundreds of items just to find what they need. Curation is where the value is.
When considering the four aspects mentioned by Brian, don’t improve things for the sake of improving them. Adding 25 mediocre tips to an existing list of 25 doesn’t make it “better.” Likewise for changing the publish date or adding a few low-quality illustrations.
Example: My colleague, Chris Haines, recently published a post on the best niche site ideas. Even though he only included 10, he has already outperformed the other “skyscraper” articles:
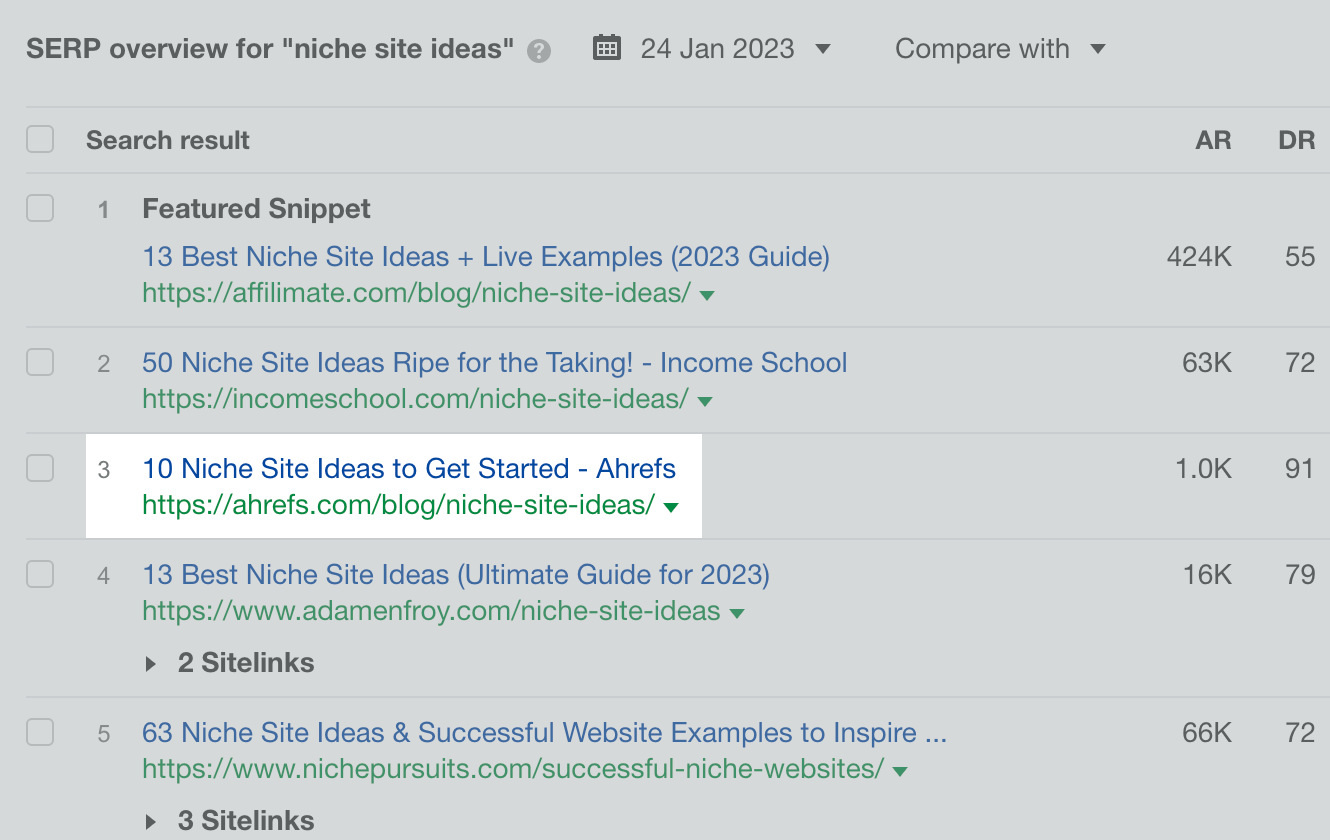
He differentiated himself through his knowledge and expertise. After all, Chris has 10 years of experience in SEO.
So when you’re creating your article, always look at any improvement through the lens of value:
Are you giving more value to the reader?
5. Not considering brand
As Ross Hudgens says, “Better does not occur in a branding vacuum.”
Most of the time, content isn’t judged solely on its quality. It’s also judged by who it comes from. We discovered this ourselves too when we tried to build links to our keyword research guide.
Most of the time, people didn’t read the article. They linked to us because of our brand and reputation—they knew we were publishing great content consistently, and they had confidence that the article we were pitching was great too.
In other words, there are times where no matter how hard you “skyscraper” your content, people just won’t link to it because they don’t know who you are.
Having your own personal brand is important these days. But think about it: What is a “strong brand” if not a consistent output of high-quality work that people enjoy? One lone skyscraper doesn’t make a city; many of them together do.
What I’m saying is this: Don’t be discouraged if your “skyscraper” article gets no results. And don’t be discouraged just because you don’t have a brand right now—you can work on that over time.
Keep on making great content—skyscraper or not—and results will come if you trust the process.
“Rome wasn’t built in a day, but they were laying bricks every hour.”
Final thoughts
The Skyscraper Technique is a legitimate link building tactic that works. But that can only happen if you:
Any questions or comments? Let me know on Twitter.


